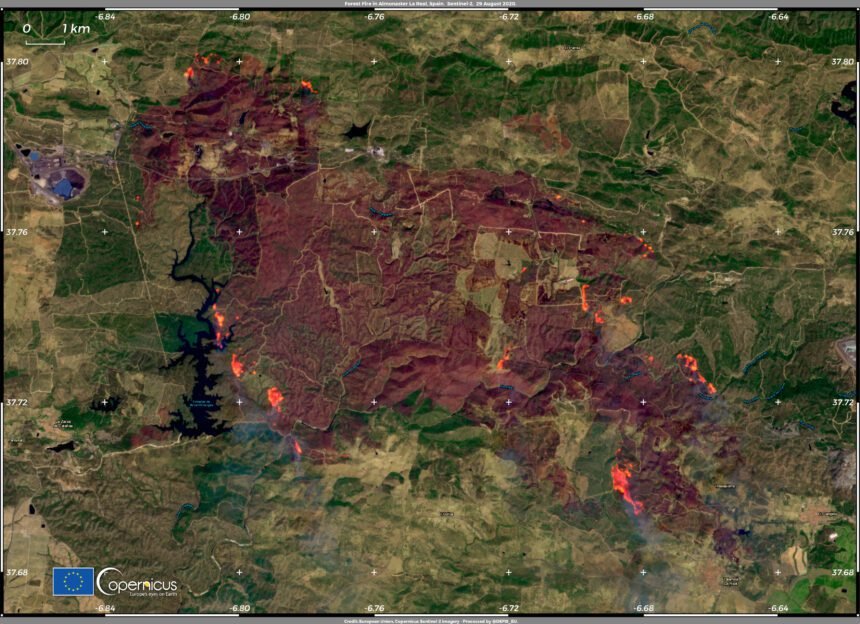
A severe heatwave sweeping the Iberian Peninsula has triggered widespread wildfires across Spain and Portugal, consuming thousands of hectares of forests, agricultural lands, and rural areas. Firefighters are contending with rapidly spreading fires fueled by extreme temperatures, drought, and high winds, while authorities have issued multiple evacuation orders to protect affected communities. The environmental and economic impacts are significant, with long-term recovery efforts focusing on improved wildfire prevention and climate adaptation strategies.
As the relentless heatwave scorches the Iberian Peninsula, vast wildfires have erupted across Spain and Portugal, engulfing forests and threatening communities. The merciless sun fuels the flames, turning once serene landscapes into battlefields of smoke and ash. Amidst the sweltering temperatures and parched earth, firefighters and residents grapple with the devastating force of nature, underscoring the fragile balance between climate extremes and the environment.
Wildfires Tear Through Iberian Landscapes Amid
Blistering temperatures and parched landscapes have set the stage for uncontrollable blazes across the Iberian Peninsula. Spain and Portugal are grappling with a series of intense wildfires that have rapidly consumed vast stretches of forests, agricultural lands, and rural communities. The relentless heatwave, marked by record-breaking highs and dry conditions, has created a tinderbox environment where flames spread with alarming speed and ferocity. Firefighters are battling not only the flames but also exhausting resources, as many regions face simultaneous emergencies.
Authorities have issued multiple evacuation orders, prioritizing the safety of residents while emergency teams strive to contain the infernos. Key factors exacerbating the crisis include:
- Extended drought periods diminishing moisture levels in vegetation
- High wind speeds accelerating wildfire expansion
- Lack of significant rainfall failing to ease the dry conditions The impact on local wildlife and ecosystems is devastating, leaving scorched earth in the fire’s path. Recovery efforts will require coordinated strategies to restore natural habitats and safeguard communities against future heatwave-induced disasters.
| Region | Area Affected (hectares) | Status | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andalusia, Spain | 15,000 | Active Containment | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alentejo, Portugal | 7,500 | Several Evacuations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Castile-León, Spain | 5,200 | Under Control
Environmental and Economic Impact on Spain andAs flames continue to sweep across vast areas of Spain and Portugal, the environmental toll is becoming increasingly evident. Thousands of hectares of forests, agricultural lands, and natural habitats have been consumed, leading to profound loss of biodiversity. The destruction of green cover exacerbates soil erosion, reduces carbon sequestration capabilities, and disrupts local ecosystems. Communities reliant on forestry and farming face long-lasting repercussions, as contaminated soil and ash make land recovery a slow and costly process. Additionally, air quality has drastically declined, posing health risks to residents and wildlife alike. The economic ramifications ripple through affected regions, impacting livelihoods and local economies. Tourism, a critical source of income for many towns, suffers due to closures and safety concerns. Small businesses, especially in rural areas, face revenue loss while reconstruction efforts demand substantial funding and labor. The following summarizes key economic impacts: Deploying a robust combination of technology and community engagement is essential to curtail the devastating impact of wildfires. Early detection systems, utilizing near real-time satellite data from instruments like NASA’s VIIRS and MODIS, enable swift identification of flames, allowing emergency teams to act promptly and strategically. Coupling this with controlled burns and vegetation management reduces the amount of fuel available, minimizing the intensity and spread of fires. Public awareness campaigns focused on educating residents about fire-safe practices-such as clearing dry brush around properties and adhering to local fire restrictions-play a pivotal role in prevention. The establishment of clear evacuation routes and advanced alert systems ensures vulnerable populations can react quickly, mitigating mortality and morbidity risks. Effective emergency response also hinges on meticulous coordination between various agencies and leveraging data-driven approaches for resource allocation. Firefighting units equipped with advanced mapping tools and particulate matter monitoring can adapt their tactics to evolving conditions on the ground. Key strategies include: As wildfires increasingly devastate regions like Spain and Portugal, proactive adaptation strategies have become essential to curbing the intensity and frequency of these disasters. Communities are turning to integrated approaches that blend traditional knowledge with innovative technologies. Critical actions include: Climate adaptation policies must also prioritize landscape restoration, ensuring ecosystems can better withstand heatwaves and prolonged droughts-key drivers of wildfire escalation. The following table highlights some essential components for future wildfire risk mitigation: |